U.S. NAVAL AVIATION RESOURCE CENTER > FIGHTERS > PREVIOUS PAGE
Design & Development
The design's potential for supersonic performance and reduced transonic drag stirred interest in the U.S. Navy. By 1953, redesigns led to a completely new aircraft bearing no more than a familial resemblance to the Cougar. The new wing had full-span leading edge slats and trailing edge flaps with roll control achieved using spoilers rather than traditional ailerons. For storage on aircraft carriers, the F-11 Tiger's wings manually folded downwards. Anticipating supersonic performance, the tailplane was all-moving. The aircraft was designed for the Wright J65 turbojet, a license-built version of the Armstrong Siddeley Sapphire.
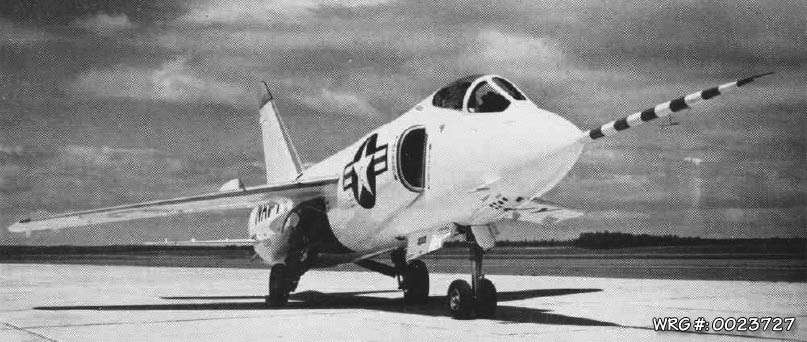
XF9F-9 prototype.
[Source: U.S. Navy photo]
The F-11 Tiger is noted for being the first jet aircraft to shoot itself down. On 21 September 1956, during a test-firing of its 20 mm (.79 in) cannons, pilot Tom Attridge fired two bursts midway through a shallow dive. As the velocity and trajectory of the cannon rounds decayed, they ultimately crossed paths with the Tiger as it continued its descent, disabling it and forcing Attridge to crash-land the aircraft; he survived.
In the late 1950s, the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) evaluated the F-11-1F as a replacement for the F-86 Sabre, then its primary jet fighter. World War II Spitfire pilot, and later honorary colonel, R.G. (Bob) Middlemiss, W/C (Ret) DFC, CD, SSM, and RCAF test pilot Jack Woodman, proceeded to California to evaluate the top two contenders, the Lockheed F-104 and the Grumman F-11F-1F at Edwards AFB. As a result of their recommendations, the Canadian government selected the F-104.
In addition to the F-11A (F11F-1) fighter, Grumman also proposed a more advanced version of the airframe known as the F11F-1F Super Tiger. This was the result of a 1955 study to fit the new General Electric J79 engine into the F11F-1 airframe.
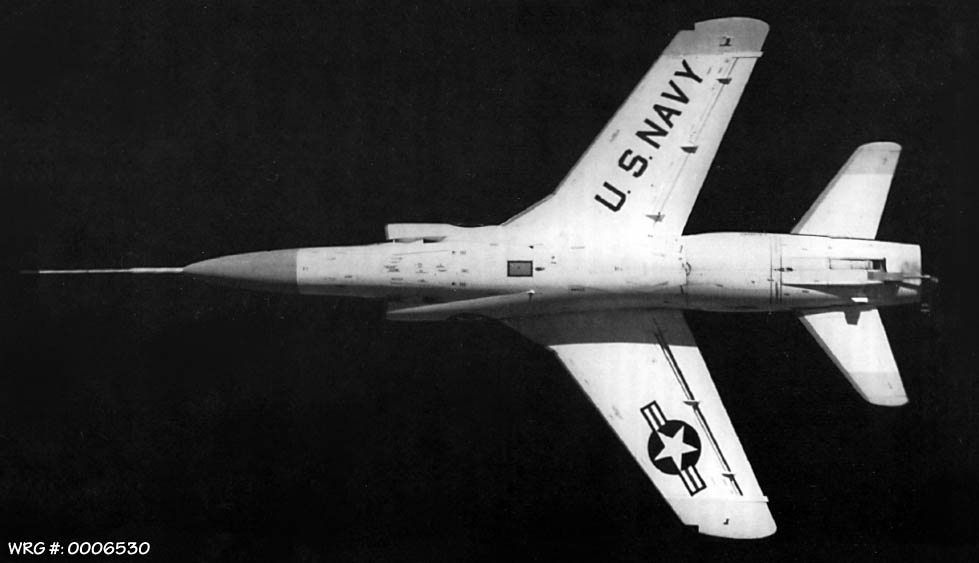

F11F-1F Super Tiger prototype photographed from below.
[Source: NACA/NASA photo]
Sources:
Wikipedia: Grumman F-11 Tiger
U.S. NAVAL AVIATION RESOURCE CENTER > FIGHTERS > PREVIOUS PAGE
